Database Configuration
An isCOBOL UDBC database is a resource that allows you to perform SQL queries on COBOL data files through a File Server service.
You can have one or more databases pointing to different File Servers or to the same File Server with different settings.
On Windows machines databases are described in the Windows registry, in the key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Veryant\UDBC. Each subkey identifies a database and subkey values are the database entries.
On Unix machines instead databases are described in an ini file that is the first applicable found in:
1. /etc/udbc.ini
2. $home/.udbc.ini
The ini file uses the following syntax:
[DATABASE-NAME] entry=value ... entry=value |
Note - for your convenience the graphical UDBC Configuration Tool is provided.
The following table describes all the available entries:
Entry | Meaning | Default if not set |
Host | IP or name of the server where the isCOBOL File Server is listening | 127.0.0.1 |
Port | port where the listening isCOBOL File Server | 10997 |
EfdDirectory | folder with EFD dictionaries on the server where UDBC Server is started. Use quotes to delimit paths with spaces. | |
FilePrefix | list of directories where files are located on the server where the isCOBOL File Server is listening. Use the server path separator to separate multiple paths. Use quotes to delimit paths with spaces. | |
FileSuffix | suffix of data files, if used. | |
FileCase | case of file names on the server, set to one of the following values: 0 (unchanged) 1 (lower case) 2 (upper case) | 0 |
CblFlags | data compatibility flags, set to one of the following values: -Dca (Acucobol) -Dci (IBM) -Dcm (Micro Focus) -Dcn (same as -Dci, but the positive COMP-3 items use x0B as the positive sign value instead of x0C) | -Dca |
CharSet | server charset, set to one of the following values: ANSI OEM | ANSI |
JulianBaseDate | base date to calculate julian dates (a julian date is the number of days between the base date and the current date) | 1900/01/01 |
SignedIndex | support signed data-items in keys. Possible values are: Yes No negative values in signed indexes might cause wrong data ordering so you should set this field to Yes only if you have signed data-items in file keys but there are no negative values | No |
StringsNotNull | convert spaces and low values to NULL and vice versa. Possible values are: Yes No | No |
MaxOpenCache | number of file definitions cached by UDBC. If the file definition is cached, then UDBC doesn’t need to read the EFD dictionary again. It speeds up performance but avoids modifications to the EFD to be active until the next reboot of the UDBC Server | 0 |
ReadOnly | avoid data modification through SQL. Possible values are: Yes No | Yes |
SqlTrace | log SQL activity to the file veryantUDBC.log in the temp directory. On Linux/Unix /tmp is used. On Windows, the GetTempPath function is called; this function checks for the existence of environment variables in the following order and uses the first path found: The path specified by the TMP environment variable. The path specified by the TEMP environment variable. The path specified by the USERPROFILE environment variable. The Windows directory. Possible values are: Yes No | No |
UDBC Configuration Tool
isCOBOL UDBC is provided with a graphical utility that allows you to manage databases.
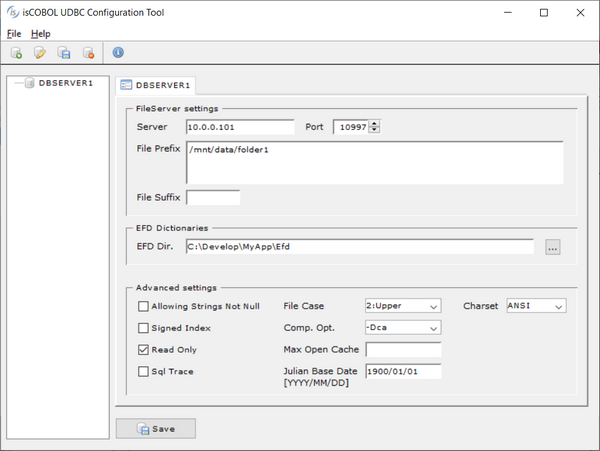
• Click on the New Database button in order to create a new database. Input a name of your choice and then compile the fields on the right providing File Server coordinates and the EFDs dictionaries location
• Click on the Rename Database button or double click on database name in the tree in order to rename the selected database.
• Click on the Delete Database button or press DEL in order to remove the selected database.
• Click on the Save button to save the latest changes you made on database settings.
The utility updates the Windows Registry or udbc.ini depending on the system when you run it.